Recent Posts
Subscribe
Sign up to get update about us. Don't be hasitate your email is safe.

 Article
Article
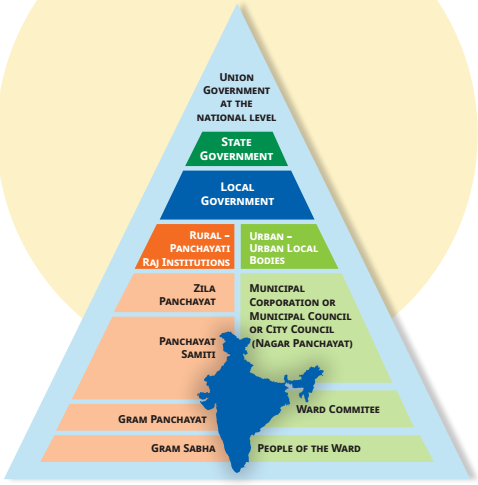
Main article: Local government in India
Local government in India is governmental jurisdiction below the level of the state. Local self-government means that residents in towns, villages and rural settlements are the people who elect local councils and their heads authorising them to solve the important issues. The 73rd and 74th constitutional amendments give recognition and protection to local governments and in addition each state has its own local government legislation.
Since 1992, local government in India takes place in two very distinct forms. Urban localities, covered in the 74th amendment to the Constitution, have Municipality but derive their powers from the individual state governments, while the powers of rural localities have been formalized under the panchayati raj system, under the 73rd amendment to the Constitution.
Main article: Municipal governance in India
The following 3 types of democratically elected urban local governance bodies in India are called municipalities and abbreviated as the "MC". These are classified based on the size of the population of the urban settlement.
Rural Local Governing Bodies
Main article: Panchayati raj in India
The Constitutional (73rd Amendment) Act, 1992 aims to provide a three-tier system of Panchayati Raj for all States having a population of over 2 million, to hold Panchayat elections regularly every five years, to provide reservation of seats for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and Women, to appoint State Finance Commission to make recommendations as regards the financial powers of the Panchayats and to constitute District Planning Committee to prepare a draft development plan for the district.[13] The following 3 hierarchies of PRI panchayats exist in states or Union Territories with more than two million inhabitants:
Main article: Elections in India
Elections in the Republic of India include elections for
Main article: Election Commission of India
The Election Commission of India (ECI) is a constitutional body established by the Constitution of India empowered to conduct free and fair elections in India. The Election commission is headed by a Chief Election Commissioner and consists of two other Election Commissioners.
At the states and union territories, the Election Commission is assisted by the Chief Electoral Officer of the state or union territory (CEO), who leads the election machinery in the states and union territories. At the district and constituency levels, the District Magistrates/District Collectors (in their capacity as District Election Officers), Electoral Registration Officers and Returning Officers perform election work.
The Election Commission operates under the powers granted by Article 324 of the Constitution and subsequently enacted Representation of the People Act. The state election commissions are responsible for conducting local body elections in the respective states. The election commission decides the dates for the filing of nominations, voting, counting and announcement of results.
A law for the registration process for political parties was enacted in 1989. The registration ensures that the political parties are recognized as national, state and regional parties. The election commission has the right to allot symbols to the political parties depending on the status. The same symbol cannot be allocated to two political parties even if they do not contest in the region.
The commission prepares electoral rolls and updates the voter list. To prevent electoral fraud, Electors Photo Identity Cards (EPIC) were introduced in 1993. However certain legal documents such as ration cards have been allowed for voting in certain situations.